CSS学习
CSS简介
如何学习
| [CSS3 教程 | 菜鸟教程 (runoob.com)](https://www.runoob.com/css3/css3-tutorial.html) |
- CSS是什么
- CSS怎么用(快速入门)
- CSS选择器(重点+难点)
- 美化网页(文字,阴影,超链接,列表,渐变)
- 盒子模型
- 浮动
- 定位
- 网页动画,特效(与Java学习无关)
什么是CSS
Cascading Style sheet 层叠级联样式表
CSS:表现层 (美化网页)
字体,颜色,边距,高度,宽度,背景图片,网页定位,网页浮动
CSS发展史
CSS1.0
CSS2.0 DIV(块) + CSS, HTML与CSS结构分离的思想,网页边简单,有利于SEO
CSS2.1 浮动,定位
CSS3.0 圆角,阴影,动画… 浏览器兼容性~
CSS快速入门
标准项目结构
style
<!--规范,<style可以编写css的代码,每一个声明最好使用分号结尾
语法:
选择器{
声明1;
声明2;
声明3;
}
-->
<style>
h1{
color: red;
}
</style>
建议采用这种规范
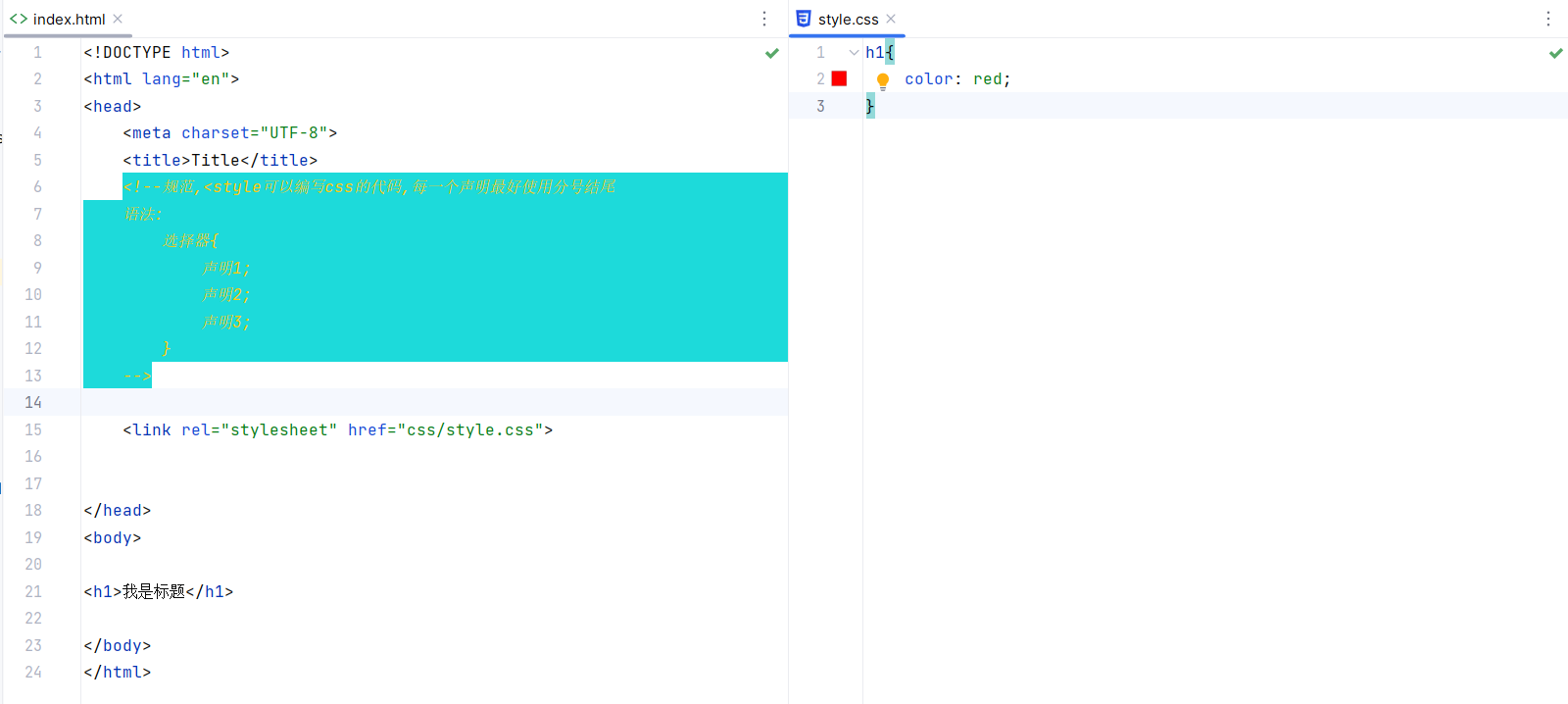
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
h1{
color: red;
}
css优势:
- 内容和表现分离
- 网页结构表现统一,可以实现复用
- 样式十分丰富
- 建议使用独立于html的css文件
- 利用SEO,容易被搜索引擎收录
VUE框架:使用后网站及其不容易被搜索引擎搜到
CSS的三种导入方式
优先级:就近原则,哪种样式离得近就用那个,准确来说是下面的覆盖上面的
- 行内样式
- 内部样式
- 外部样式
<!--行内样式,在标签元素中,编写一个style属性,编写样式即可-->
<h1 style="color: red">我是标题</h1>
<!-- 内部样式表-->
<style>
h1{
color: green;
}
</style>
<!-- 外部样式链接-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
/* 外部样式表*/
h1{
color: yellow;
}
拓展:外部样式两种写法
-
链接式 html标签
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css"> -
导入式
@import是CSS2.1特有的,弊端先加载网页框架,再渲染样式
<style> @import url("css/style.css"); </style>
选择器
作用:选择页面上的某一个或某一类元素
基本选择器
-
标签选择器:选择一类标签 标签名{}
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> /*标签选择器,会选择到页面上所有这个标签的元素*/ <style> h1{ color: #a13d30; } p{ font-size: 80px; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>学Java</h1> <h1>学Java</h1> <p>听狂神说</p> </body> </html> -
类选择器 class: 选中所有class属性一致的标签,跨标签 .类名{}
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /*类选择器的格式 .class的名称{} 好处:可以多个标签归类,是同一个class,可以复用 */ .monki{ color: red; } .ssh{ color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 class="monki">标题1</h1> <h1 class="ssh">标题2</h1> <h1>标题3</h1> <p class="ssh">test</p> </body> </html> -
id选择器: id必须为全局唯一! #id名{}
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* id选择器 : id必须保证全局唯一! #id名称{} 优先级:id选择器>class选择器>标签选择器 */ #monki{ color: red; } .style{ color: green; } h1{ color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 id="monki" class="style">标题1</h1> <h1 class="style">标题2</h1> <h1 class="style">标题3</h1> <h1>标题4</h1> <h1>标题5</h1> </body> </html>
优先级:id > class >标签
层次选择器
-
后代选择器:在某个元素的后面 祖爷爷 爷爷 爸爸 你 作用于某个元素的 所有子元素(包含子元素的后代)
/*后代选择器*/ body p{ background: red; } body ul li{ background: red; } -
子选择器:只有一代 作用于某个元素下面的 作用于某个元素的下一代元素(不包含子元素后代)
/*子选择器*/ body>p{ background: cadetblue; } -
相邻兄弟选择器
/*相邻兄弟选择器 只有一个,相邻(向下)*/ .active + p{ background: brown; } -
通用兄弟选择器
/*通用兄弟选择器 : 当前选中元素向下的所有兄弟元素*/ .active~p{ background: antiquewhite; }
结构伪类选择器
伪类: 条件
/*ul的第一个子元素*/
ul li:first-child{
background: brown;
}
/*ul的最后一个子元素*/
ul li:last-child{
background: yellow;
}
/*选中p1:定位父元素,选中当前的第一个元素
选择当前p元素的父级元素,选中父级元素的第一个,并且这个元素是p元素才生效
*/
p:nth-child(1){
background: red;
}
body p:first-child{
background: aquamarine;
}
/*选中父元素下的p元素的第二个*/
p:nth-of-type(2){
background: blue;
}
/*悬停*/
a:hover{
background: aqua;
}
属性选择器(常用)
结合了 id + class
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.demo a{
float: left;
display: block;
height: 50px;
width: 50px;
border-radius: 10px;
background: blue;
text-align: center;
color: white;
text-decoration: none;
margin-right: 5px ;
font: bold 20px/50px Arial;
}
/* 属性名 / 属性名=属性值(正则)
= 绝对等于
*=包含这个元素
^=以这个开头
$=以这个结尾
*/
/*存在id属性的元素 a[]{}*/
a[id]{
background: yellow;
}
a[id=first]{
background: aqua;
}
/*class中有links的元素*/
a[class*=links]{
background: black;
}
/*选中href中以http开头的元素*/
a[href^=http]{
background: yellow;
}
/*选中herf属性以pdf结尾的元素*/
a[href$=pdf]{
background: blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="demo">
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="links item first" id="first">1</a>
<a href="http://monkifantasy.me" class="links item active" target="_blank" title="tset">2</a>
<a href="images/123.html" class="links item">3</a>
<a href="images/123.png" class="links item">4</a>
<a href="images/123.jpg" class="links item">5</a>
<a href="abc" class="links item">6</a>
<a href="/a.pdf" class="links item">7</a>
<a href="abc.pdf" class="links item">8</a>
<a href="abc.doc" class="links item">9</a>
<a href="abcd.doc" class="links item last">10</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>
= 绝对等于
*=包含这个元素
^=以这个开头
$=以这个结尾